Ratio Put Spread
Usually entered when market is near B and you expect market to fall slightly to moderately, but see a potential for sharp rise. One of the most common option spreads, seldom done more than 1:3 (two excess shorts) because of downside risk.
Overview
Pattern evolution:
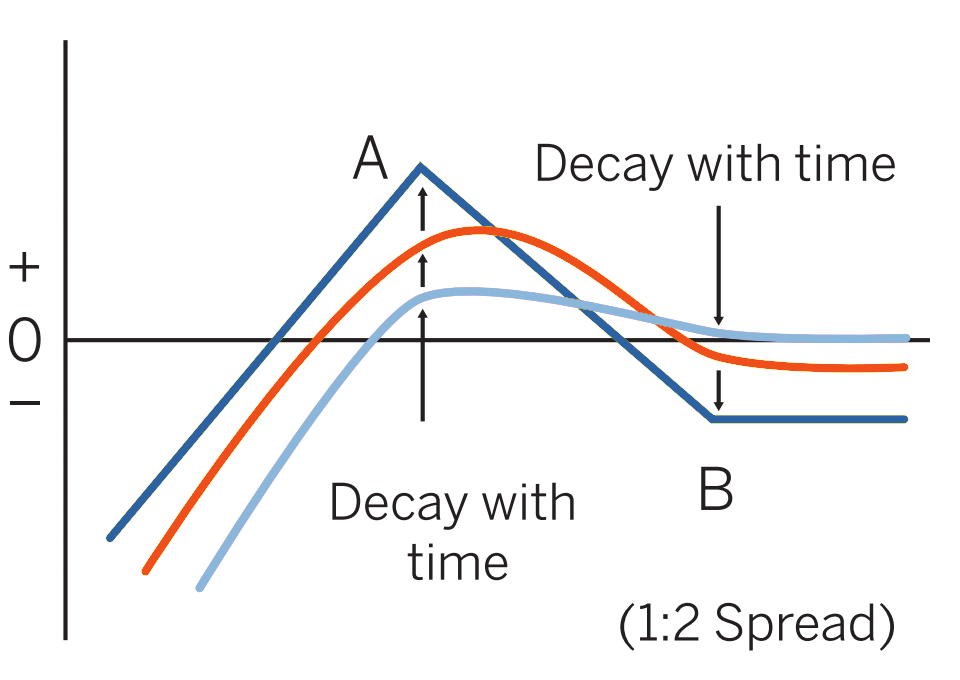
When to use: Usually entered when market is near B and you expect market to fall slightly to moderately, but see a potential for sharp rise. One of the most common option spreads, seldom done more than 1:3 (two excess shorts) because of downside risk.
Profit characteristics: Maximum profit in amount of B – A – net cost of position (for put-vs.-put version), realized if market is at A at expiration, or B – A + net credit of position (if long option premium is less than premium collected from the sale of two or more options).
Loss characteristics: Loss limited on upside (to net cost of position in put-vs.-put version, or no loss if position established at a credit) but open-ended if market falls. Rate of loss, if market falls below strike price A, is proportional to number of excess shorts in position.
Decay characteristics: Dependent on the net time value purchased or sold via this strategy. If more time value sold than bought, then time value decays work to the benefit of the holder.
CATEGORY: Precision
Long put B, short puts A
For example long 1 put @ B; short 2 puts @ A
Example
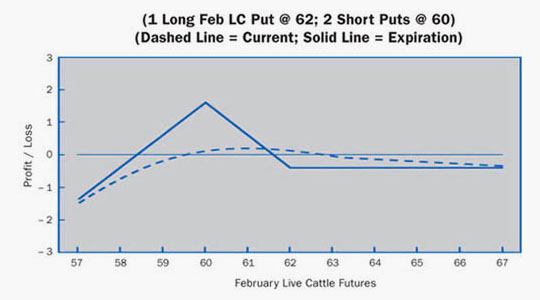
Scenario:
This trader feels that current implied volatility is at relatively high levels. The thinking here is that the market should consolidate after its big drop. The trader now believes reduced volatility and a slow downward drifting of price are likely. Consequently, an order to execute a ratio put spread is placed with the broker.
Specifics:
Underlying Futures Contract: February Live Cattle
Futures Price Level: 62.50
Days to Futures Expiration: 30
Days to Option Expiration: 20
Option Implied Volatility: 15.5%
Option Position:
| Long 1 Feb 62.00 Put | – 0.675 ($270.00) |
| Long 1 Dec 1.0000 Put | |
| Short 2 Feb 60.00 Puts | + 0.150 ($ 60.00) x 2 |
| – 0.375 ($150.00) |
At Expiration:
Breakeven: 58.375 (60.00 strike – difference between strikes + 0.375 debit).
Loss Risk: Unlimited; losses continue to mount as futures fall below 58.375.
Potential Gain: Maximum gain of 1.625 ($650) peaks at 60.00 strike.
Things to Watch:
Be very sure that prices will not go into a sharp decline. But, if a slow drop is anticipated this may be a good strategy. A rally will produce a small gain or loss depending on the strikes chosen.
Additional Futures & Options Strategies
- Long Futures
- Long Synthetic Futures
- Short Synthetic Futures
- Long Risk Reversal
- Short Risk Reversal
- Long Call
- Short Call
- Long Put
- Short Put
- Bear Spread
- Bull Spread
- Long Butterfly
- Short Butterfly
- Long Iron Butterfly
- Short Iron Butterfly
- Long Straddle
- Short Straddle
- Long Strangle
- Short Strangle
- Ratio Call Spread
- Ratio Call Backspread
- Ratio Put Backspread
- Box or Conversion
- Futures & Options Strategies Overview
Contents Courtesy of CME Group.
