There are various exotic option strategies with different objectives and theoretical scenarios. I’m going to walk you through the basics in detail, while keeping these complex instruments as simple as possible! In addition, over the next few weeks, we will cover a few prime options strategies for futures traders that benefit from the leverage and volatility inherent to our markets.
Let’s start with an option tree, or otherwise known as “Christmas Tree”. It is called a tree because when drawn structurally, this three-legged option play will form a triangle. Options are risky no matter what strategy you employ, and this option tree has unlimited risk potential. A trader should carefully consider if this strategy is suitable for their risk tolerance.
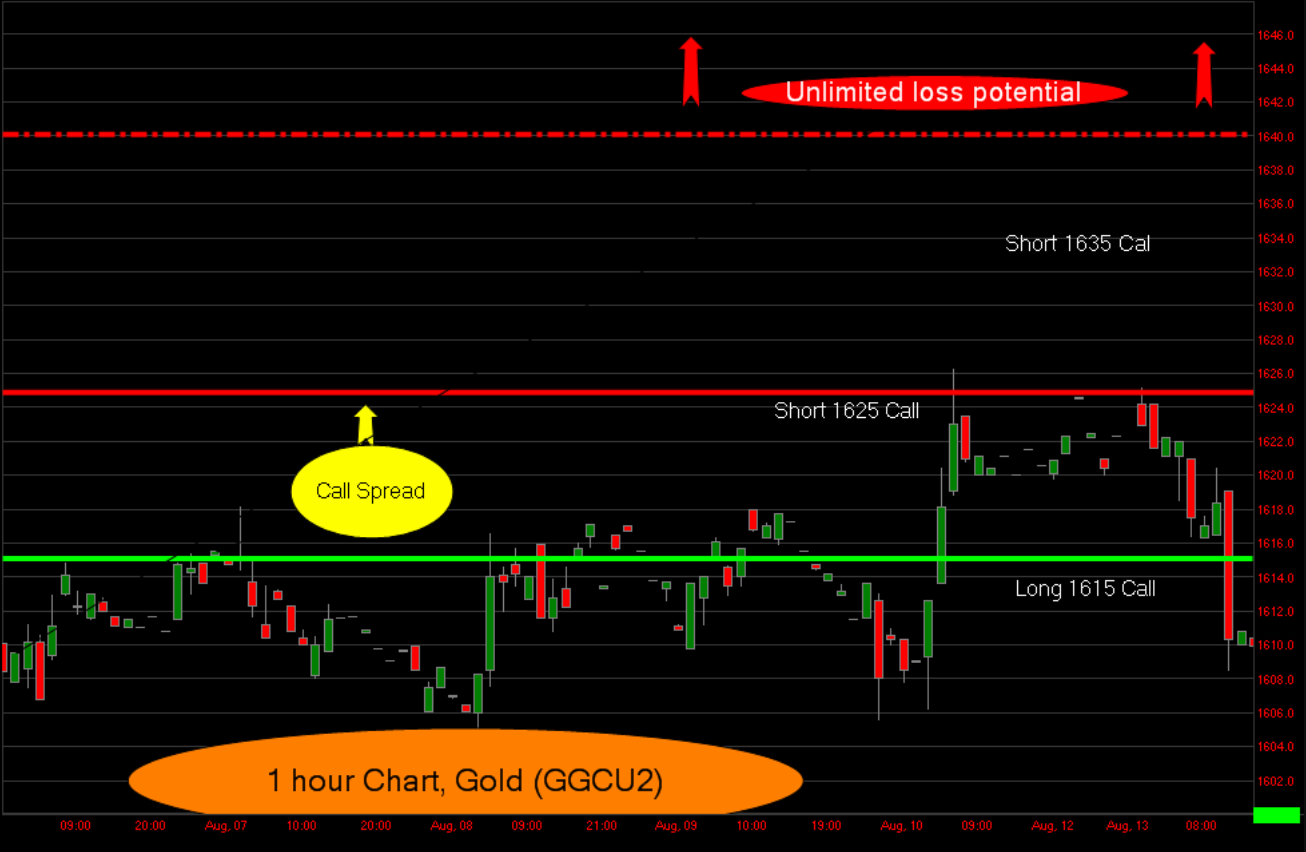
The Plan: We would purchase an option, and sell two other options at successively higher strike prices.
Example: Call option tree on September Gold futures contract.
Buying the 1615 call or Buy a put
Selling the 1625 call or Sell a put
Selling the 1635 call or Sell a put
Maximum Loss: If held to expiration, the loss starts at 1645 +/- premium collected/paid.
Maximum Gain: The profit from the bull spread +/- the premium collected.
Any trades are educational examples only. They do not include commissions and fees.
All the legs must either be calls (Call tree) or puts (Put tree).
When to use it: A trader would use this strategy when he/she thought the underlying —in this case gold— was going to make a move higher, but not as high as the second short option position. Conversely, a trader could use a Put option tree if he/she thought the market was headed lower. This uncovered short option presents unlimited risk to the trader if left unmanaged and could cause serious damage to the trader.
The Goal: The ultimate purpose of using this strategy is to use the premium of short options to finance the purchase of the call option as well as collect the premium at expiration. We want two things to happen:
- Finance the purchase of the call option
- Collect the option premium at expiration
Things to consider:
- A plan to exit this trade if the market turns against you.
- Time until expiration – specifically because of the short option leg.
- Theta – the time decay associated with an option. It signifies how much intrinsic value is whittled away as time passes.
- Delta of the option position – Delta is the percentage move of the option in correlation to the futures contract.
- Risk tolerance.
Any trades are educational examples only. They do not include commissions and fees.
Options can be great tools to utilize in trading the futures markets. Options are flexible but complex instruments that involve complex mathematics and theoretical scenarios that one should understand before trading in a live environment. If you have any questions or want to begin using such strategies, download the guide below and contact your StoneX Broker.
